GPU scaling adjusts the horizontal and vertical plane of the video or image to best fit the screen without compromising on the aspect ratio. Users have several scaling options depending on their gaming preferences: preserved, centered, and full panel.
What is GPU Scaling?
GPU scaling is an option found in the configuration menus of graphical processor units (GPUs). GPU scaling rectifies aspect ratio disparity (an image's width in relation to its height) that happens between the software that generates the image (application or game) and the output device's resolution (monitor).
GPU scaling is often used to take the output of an older game that was designed with a 4:3 or 5:4 aspect ratio and convert it to fit on a 16:9 aspect ratio without stretching the picture horizontally.
GPU Scaling Types/Options
There are three main GPU scaling methods: Maintain aspect ratio, Use centered timings, and Scale Image to Full Panel Size.
"Maintain Aspect Ratio" or "Aspect Ratio"
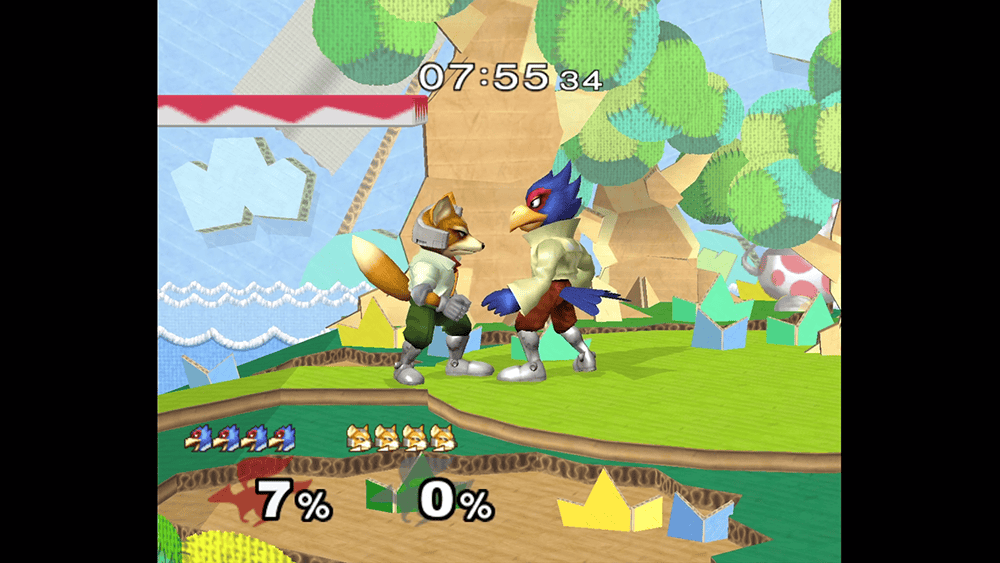
As the name suggests, "Maintain Aspect Ratio" is able to fill the screen without stretching the image. Black bars are placed either on the top and bottom or left and right of the picture.
To illustrate: At a resolution of 1280x1024 (5:4), the screen will feature black bars on the left and right side.
Use Centered Timings or "Full-Screen"
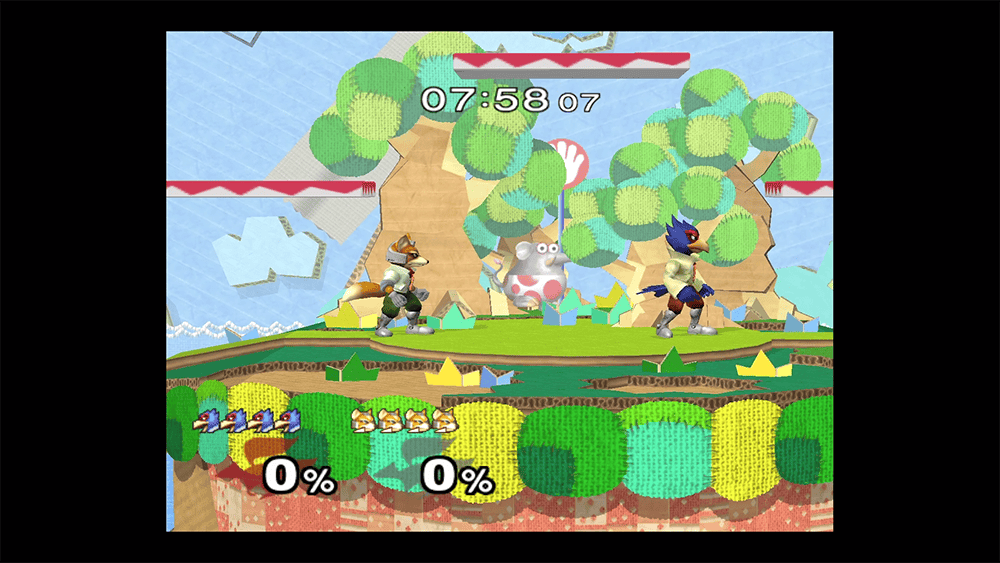
"Use centered timings" or "centered" will turn off image scaling and center the image on non-native resolutions. As a result, black bars may appear around the image.
To illustrate: A 24" monitor (1920x1200 native resolution) at a resolution of 1680x1050 (16:10 aspect ratio) or lower will result in a black border around the monitor.
Scale Image to Full Panel Size or "Full-Screen"

"Scale image to full panel size" will expand the current image to the size of the monitor for non-native resolutions.
To illustrate: A monitor with a resolution of 1280x1024 (5:4), the screen will stretch to fill the screen.
Underscan and Overscan
An underscan is a behavior where the image rendered on the display is smaller than the physical area of the screen. As a result, a black border is created around the image.
An overscan is a behavior where the image rendered on the display extends outside the visible bounds of the screen.
GPU Scaling and Lag
There are two main ways that scaling is performed: GPU and Monitor.
Generally speaking, GPU scaling results in more input lag as it requires extra processing. The amount of input lag is negligible for something like videos, however it may be noticeable when playing games.
If your monitor supports it, you should opt to use display scaling.
Enabling GPU Scaling with AMD Catalyst Control Center
- From the desktop, right click anywhere and select "AMD Radeon Settings" from the drop down menu.
- Select "display" from the menu.
- Toggle the GPU Scaling option to "On." The screen will go black while GPU scaling is enabled.
- Once GPU scaling is enabled, you can select your scaling preference via the "Scaling Mode" dropdown; Your scaling options are Preserve aspect ratio, Full Panel, and Center.
Enabling GPU Scaling with an NVIDIA Graphics Card
- From the desktop, right click anywhere and select "Nvidia Control Panel" from the drop down menu.
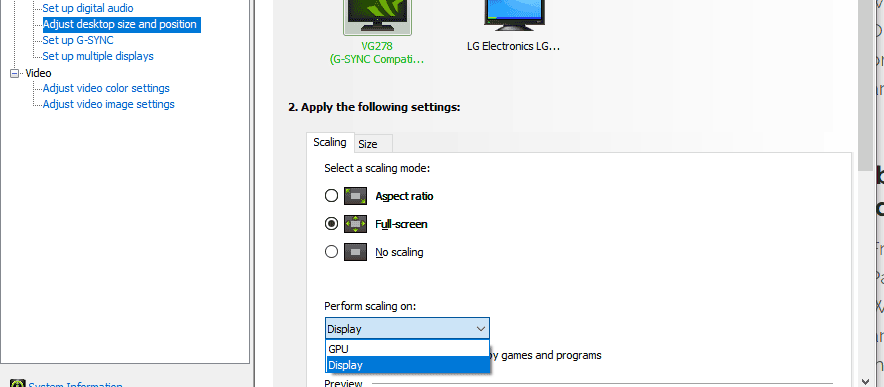
- With the NVIDIA Control Panel open, click "Adjust Desktop Size and Position" from the left "Display" sub-menu.
- In the Adjust Desktop Size and Position menu, under "Perform Scaling on" select GPU from the drop-down menu.
- From there you can also select your scaling preference: Aspect Ratio, Full-Screen, or No Scaling.

